The comprehensive testing of cannabis products can involve numerous stages. Typically, laboratories will test for residual levels of solvents, contaminants (chemical, microbial and physical contaminants), the potency of the product, and for terpenes.1 Testing for potentially harmful microbes is extremely important because many of these organisms are known health hazards.
The sources of contamination from microbes will typically occur from two different categories2:
- Cultivation
- Handling and packaging
During cultivation, microbial contamination can come from water, other nutrients, and from us, handling the plant. Once the crop has been harvested, microbes can be introduced into the cannabis by people who are in contact with it.
To avoid microbial contamination, the packaging and handling of cannabis products needs to follow specific routines, such as working in clean areas on sterile surfaces, and handlers must wear gloves.1, 3
Common microorganisms that labs test for include: 1, 3
- Salmonella is a bacterium that thrives in the intestines of animals and in people. Salmonellosis is an illness that occurs when live Salmonella bacteria enter a person’s body. The bacteria will often attach itself to the lining of the intestinal tract and release toxins that attack intestinal cells.
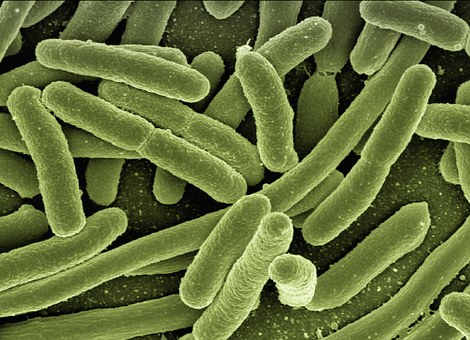
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) is another bacterium found in the intestines of animals and people. Some types of E. coli may be relatively harmless and some can be extremely dangerous such as E. coli O157:H7. Symptoms of an intestinal infection from E. coli virus include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fever. When the infestation is severe, one can suffer from dehydration, bloody diarrhea, and even renal failure (kidney failure).
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a bacterium that can cause usually relatively mild symptoms that can include body aches, fever, chills, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and decreased urination.
- Clostridium botulimum is a spore-forming bacterium that produces an extremely potent toxin. Botulism poisoning can cause paralysis and even death in those infected.
Cannabis can also be tested for water activity to help ensure product safety. Water activity is the ratio of the partial vapor pressure of water in the material to the partial vapor pressure of pure water at the same temperature.What this means is that water activity is a measure of the moisture in a product that is available for microbial growth. Water molecules that are not bound can support potentially harmful bacteria.3
References
- Thomas, B. F., & ElSohly, M. (2015). The analytical chemistry of cannabis: Quality assessment, assurance, and regulation of medicinal marijuana and cannabinoid preparations. Elsevier.
- Ilias, Y., Rudaz, S., Mathieu, P., Christen, P., & Veuthey, J. L. (2005). Extraction and analysis of different Cannabis samples by headspace solid‐phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography‐mass spectrometry. Journal of separation science, 28(17), 2293-2300.
- Unger, P., Brauninger, R., Hudalla, C., Holmes, M., & Sherman, B. (2014). Standards for Cannabis Testing Laboratories. Eugene, OR: Cannabis Safety Institute. Retrieved, 4(01), 2016.